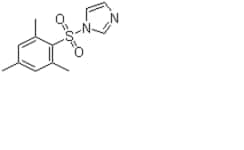
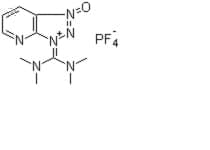
Showing 1–10 of 169 results
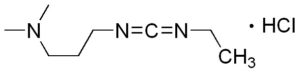
EDC·HCl (EDC, EDAC or EDCI) is a water-soluble carbodiimide coupling reagent that can be used in aqueous phase to facility the activation of a carboxyl group. It also simplifies the purification of the coupling reaction as the byproduct from EDC is also water soluable which makes it more convenient to be removed. EDC is often used in combination with HOBt or HOSu.
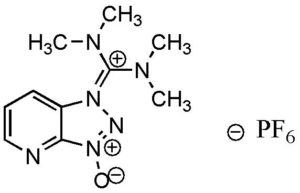
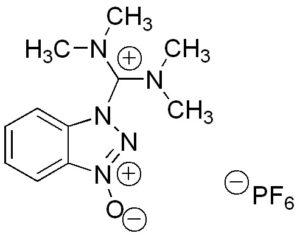
Hexafluorophosphate Azabenzotriazole Tetramethyl Uronium (HATU) is a reagent used in peptide coupling. You can purchase this chemical in three catalog sizes: 25g, 100g or 250g, but also good for bulk quantity. HATU is a key chemical used to form a coupling reaction, creating a formation as part of peptide synthesis.
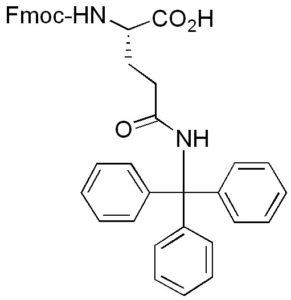
Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-OH has good solubility properties in most organic solvents, and its use has been shown to result in significantly purer peptides than other derivatives used for the introduction of Gln [1]. Coupling can be performed by standard procedures. The trityl-protecting group is normally removed by 95% TFA in 1-3 hours, with no alkylation of Trp. Using Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-OH in peptide synthesis prevents the possibility of the amide side chain from undergoing dehydration side reactions during activation, especially with carbodiimide reagents. Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-OH also has better solubility properties than Fmoc-Gln-OH. Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-OH dissolves readily in all standard peptide synthesis reagents, while Fmoc-Gln-OH is much less soluble in dimethylformamide (DMF).